Introduction
Blockchain is a coined term from recent years which describes a distributed ledger which is inherently immutable, scalable and transparent, providing trust in naturally trustless environments. It was originally conceived based on a variety of technologies and tools related to distributed systems such as: decentralized P2P networks, Cloud computing, Hardware virtualization. As well as having its foundation built on topics of information security such as Public-Key cryptography, digital signatures and hashing. Most of the attention blockchain is receiving in the current days is due to some popular cryptocurrency platforms such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, which are leveraging the capability of blockchain technology in many ways. Although Blockchain is strongly related to cryptocurrencies it also provides the foundation for other decentralized applications and has the potential to impact many important industrial and social segments of society since blockchain can be used in several different contexts.
Blockchain has ground-breaking potential applications in a diversity of fields: Logistics, Financial, Banking, Insurance, Healthcare, Lottery, Internet of Things, cloud storage, among others. As Blockchain merges with other fields of computer science such as AI and IoT, it could prove to be a broader platform for transparency and integrity in society, including when it comes to fighting bribery and corruption. It could also lead to new advancements in automation in supply chains and potential citizen participation in governmental decisions, such as how to allocate resources for a specific project in a city. From private organizations to government and non-profit institutes, blockchain has a positive future landscape and we're just starting to see how these related technologies will start to unfold. But many challenges lay ahead, and only a multi-party governance model, with the active participation of civilians and open source communities, can pave the way for a transparent and inclusive blockchain revolution.
What is it?
Nowadays bitcoin and its related alt-coins already caught the attention of the mainstream media, there are several websites and cryptocurrency exchanges around the world providing users the possibility to buy and sell crypto and trade online using digital assets and real money. Blockchain is the foundation for cryptocurrencies but can be leveraged far beyond the financial market and be used in several other segments of the economy.
Some researchers and scholars coined the term "Fourth Industrial Revolution" and as part of its foundational structure the blockchain revolution raises new challenges and multi-stakeholder cooperation opportunities.
So what is a Blockchain? Blockchain centers around the idea of a distributed ledger, a transparent distributed database that could potentially record any digital asset such as cryptocurrency, software tokens, private records such as company files or patient records for healthcare.
Blockchains can be either Permissioned or Permissionless. That means that all participants are known and might be identified in order to participate in the network or otherwise any participant as long as having a valid address might participate in the network (Permissionless).
To secure the distributed ledger a variety of cryptographic algorithms are used along with certain validation procedures such as Proof of Work or Proof of Stake.
When a new transaction hits the blockchain the nodes composing the P2P network validates the request ensuring that only valid transactions can be appended to the ledger.
The power of decentralization arises when it comes to scalability, being able to scale as the network grows, without having a central point of failure or a central authority. This feature along with the other inherent features of a blockchain such as transparency, immutability and security.
Features

Trust
Brings trust among multiple parties in a naturally untrustworthy environment.
Enables Transfer of Value
Enables Transfer of Value between its users through the usage of tokens.
Decentralized
Decentralized by nature through the usage of Consensus algorithms, no central authority concentrates the power of decision but instead decision is taken by the majority vote.

A platform for executing business logic
Blockchain is a platform where higher level programs can run that execute specific business logic on behalf of predefined rules set by the users of the network, the so called smart contracts.
Types of Blockchain
Blockchains can be divided in 2 types:
Permissionless
A Permissionless blockchain is considered to be public, that means that the network accepts requests from any user in the world as long as the user possesses an address, thus making it harder to achieve consensus if compared to the permissioned model, transactions might suffer longer delays to get validated, confirmed and ultimately appended to the ledger, proof of work or proof of stake algorithms are commonly used in order to validate new blocks leveraging trust between anonymous co-participants of the network. Examples of Permissionless blockchains are: Bitcoin, Ethereum.
Permissioned
A Permissioned blockchain accepts requests from authenticated nodes only, thus making it possible to achieve consensus on the transaction level, ultimately speeding up transaction processing and leveraging trust between co-participants of the network. They do provide a more simplistic approach to deliver the promised efficiencies and cost savings. Permissioned blockchains can be used within organizations, among different departments or across multiple organizations, leveraging trust between multiple private third-parties in B2B and supply-chain scenarios. Usually a permissioned blockchain platform is built using certain frameworks or collection of libraries such as: Hyperledger, Quorum and R3 Corda.
History
Blockchain originally traces back to Cloud computing and historically originates from the advent and development of several technologies
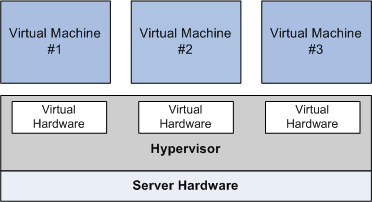
Hardware
Blockchain technology has been leveraged and benefits from the advancements in hardware technologies such as multi-core CPUs and Hardware Virtualization.
Network
It also benefits from advancements in Internet technologies (Web services, P2P networks, service-oriented architectures, Web 2.0).

Distributed Systems and Cloud Computing
Blockchain uses many concepts originated in the domain of large scale Distributed systems algorithms and design. It also benefits from the consolidation of cloud computing and virtual server provisioning.

Security
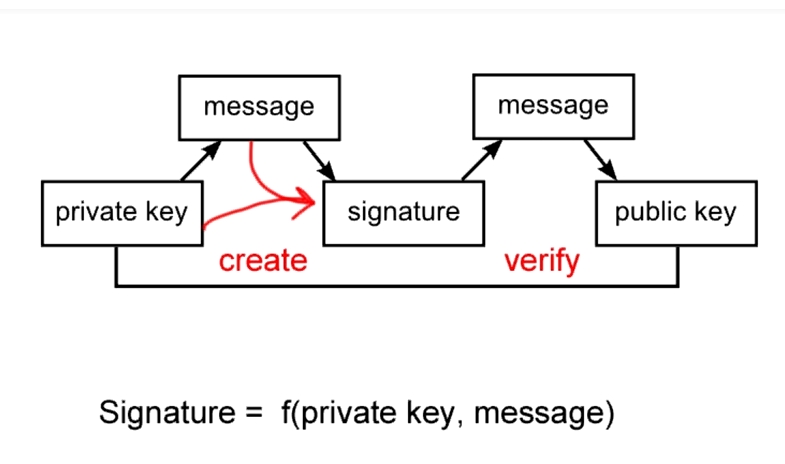
Blockchain makes use of advanced concepts of information security and it heavily relies on cryptography, digitial signatures and internet security in general.
Current challenges
Blockchain technology still faces a variety of challenges in order to achieve the goals portrayed by the visionaries of the blockchain and cryptocurrency markets, mainly in these 2 aspects:
Security
Many are the challenges when it concerns security, since in order to function properly a blockchain platform must ensure a high level standard for security using appropriate cryptographic algorithms and advanced methods for achieving consensus and making the network resilient and fault tolerant. Cryptocurrency exchanges suffer from increased targeted attacks by hackers, since many hold user wallets online, there have been incidents of hackers stealing user digital assets, incurring the loss of millions worth of crypto. Security involving wallet technology is an active topic of research nowadays by many enterprises and organizations. Since blockchains are immutable append-only structures, once a hacker transfers assets to another address it's gone, that's why security is a top priority in the cryptospace. There are also many attacks targeted to the public blockchains such as bitcoin, Ethereum and others. From spam and invalid requests to the famous 51% attack, a blockchain network must ensure it has rules in place for dealing with all the possible incidents coming from hackers or either random system behavior. Many are the challenges regarding social engineering as well, sophisticated mechanisms have been adopted by hackers in order to deceive and steal secrets from end users such as their wallet addresses and passwords. Some companies sell hardware wallets, which in theory makes it harder for a potential hacker to break in and transfer funds.
Scalability
Blockchain technology faces many challenges in order to scale properly (mainly when it comes to public blockchains such as Bitcoin, Ethereum and others.) validating blocks can be costly and time consuming, public blockchains commonly use proof of work or proof of stake in order to validate a new block which might take a considerable amount of time and might require a lot of processing power, in the other hand permissioned blockchains can be way faster when validating transactions since all participants are authenticated. In the past few years Bitcoin has suffered a staggering increase of transactions and new users, making the network sustain a transaction confirmation time in the magnitude of minutes, while also increasing transaction mining fees and costs. Lightning network is a new approach and proposal to solve some of the original Bitcoin's platform problems. Many other platforms were created in order the target the desired features that Bitcoin was lacking. Some critics argue that if cryptocurrencies can't achieve the level of speed that legacy systems have (such as credit card companies) then they will probably not be used at all. Another issue with scalability is while the ledger accepts new blocks it keeps growing and demanding more persistent storage in order for nodes to keep a full copy of the ledger, pruning and compression are some solutions to address this problem but still there are many challenges when it comes to storing the ledger as it grows.
Future trends
These are some of the future trends surrounding blockchain research and development:
Modular architectures
A future trend of blockchain as indicated by recent modern projects is to use layered, modular architectures instead of monolithic ones. Many of the components composing a blockchain platform can be broken down or split into multiple modules or layers, making it easier to change one layer without affecting others, similar to how the internet stack is built and other distributed systems, in order to mimic this successful and proven architectural approach of the internet. A modular blockchain is based on the abstraction level of the capability provided and the service model, namely: Smart contract/scripting engine, Computation layer and Settlement Layer. Each of these abstractions can also be viewed as a layered architecture where services of a higher layer can be composed from services of the underlying layer.
Artificial Intelligence
Intelligent agents are being built by several organizations and software companies in order to leverage the capabilities of Artificial intelligence. Blockchain and AI are two of the most ground-breaking technologies nowadays and researchers have started to see the potential benefits of merging these technologies in the future. AI can boost many features of blockchain such as automation, scalability, security and costs optimization.AI can leverage automated intelligent decision making agents and increase artificial trust: as soon as part of our tasks will be managed by autonomous virtual agents, having a clear audit trail will help agents to trust each other (and us to trust them). It will also eventually increase machine-to-machine interaction and transaction providing a secure way to share data and coordinate decisions
Internet of Things
Devices of all sizes and shapes are taking over the internet of the future, this industry specifically called "Internet of Things" is bringing together potential opportunities for blockchain applications. Some applications related to security are already being researched, areas such as Blockchain-based compromised firmware detection and self-healing, which uses blockchain for integrity checking, microtransactions and sensor network shared ledger are some examples. Redundancy is commonly used to heal corrupted software in sensor networks, where the same or similar code replaces the corrupted code. The compromised firmware is replaced by a “known to be good” firmware. By using the blockchain, the history of firmware can be traced. Thus, when compromised firmware is detected, it will be forced to roll back to its previous version.
Public key cryptography
Hyperledger
Bitcoin
The original blockchain paper presented by the anonymous author Satoshi Nakamoto revolutionized the industry, bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency to hit mainstream and is a good implementation of the concepts behind blockchain. BTC has seen an impressive growth in past years and still maintains itself as the top crypto platform despite challenges and current market volatility.
Ethereum
Ethereum is a public permissionless decentralized computing platform which supports smart-contracts and runs on top of a Virtual Machine model, the EVM. Ethereum uses the concepts of 2 tokens: Ether and Gas. Ether is a currency while Gas is considered a commodity. Price quotations of each one can vary independently. A certain amount of Ether can be converted to Gas. Gas is used as a fuel for the processing cost on the EVM for running any operation.
IOTA
IOTA was developed to target IoT networks and leverages the Tangle ledger which is able to settle transactions with zero fees so devices can trade exact amounts of resources on-demand, as well as store data from sensors and dataloggers securely and verified on the ledger.
Cardano
Cardano is a cryptocurrency (ADA) and a modular blockchain platform which allows smart-contracts to be executed, it is based on academic research standards such as peer reviews and uses quite strict fault tolerance and error verification mechanisms based on standards similar to those of mission critical software (airplanes, hospitals, etc) in order to minimize any possible security vulnerabilities while leveraging a safe scripting engine model based on Haskell. It promises to leverage very high security standards and enable a modular architecture for minimizing any possible hard-fork. It aims to cover limitations that first and second generation blockchains have presented along years, like addressing scalability, power consumption, extensibility, transaction confirmation response time and security.
-
Cardano - ADA
-
Cardano uses a modular architecture so different layers can be replaced or updated without affecting other layers, it also uses a new proof of stake algorithm called Ouroboros. Its features promises to leverage blockchain capabilities to the next level when it comes to scalability, security, speed, low costs and stability. At the time of writing the project is still under development.